Eustachian tubes of children have not completely developed and are structurally vulnerable to transfer inflammations from the nose to the ears easily.
In statistics, 90% of children younger than 3 years old experienced tympanitis.
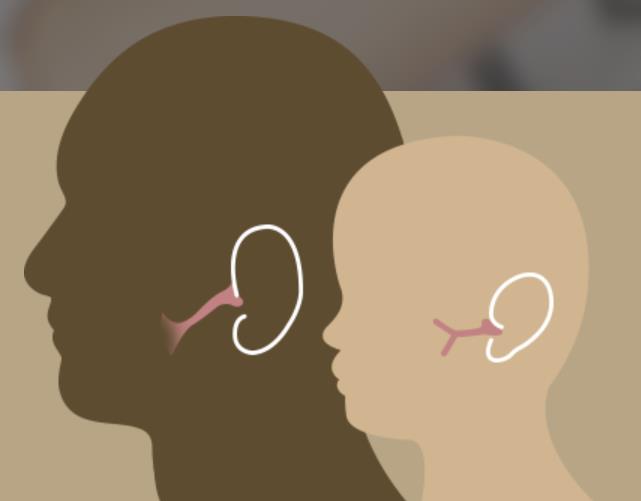
◀ Children’s eustachian tubes are more horizontal than adults, making it difficult to ventilate air and protect the ear from inflammation.

Antibiotics do not treat all tympanitis.
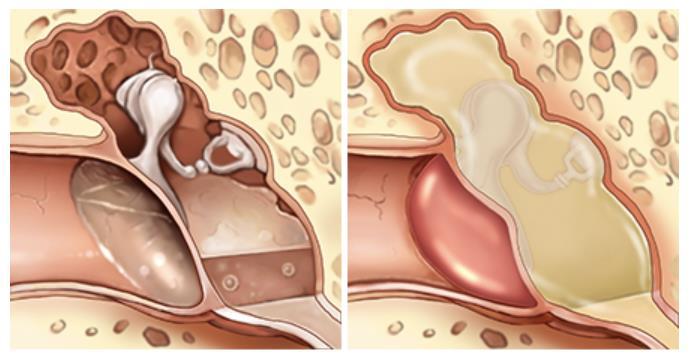
There are types of tympanitis, such as exudative and purulent. According to the manual, treating tympanitis in children does not require using antibiotics prescribed to treat exudative tympanitis. Even if a patient complains of pain, inflammation, and fever with acute tympanitis, antibiotics should not prescribed.
Types of tympanitis: exudative(left), purulent(right) ▶

The following cases require the use of antibiotics
|

Tympanitis could be controlled by managing runny nose and nasal congestion.
Healthier nasal cavities and eustachian tubes make a healthy tympanum (middle ear). The root cause of tympanitis is an unhealthy lining of nasal cavities due to inflammation and incompletely developed eustachian tubes delaying recovery.
Asina medicinal treatments treat tympanitis and recover the respiratory system. Also, our treatment goal is not for curing the symptoms; we also help boost the immune system to protect from recurring symptoms.

Hamsoa’s Tympanitis Treatment Programs
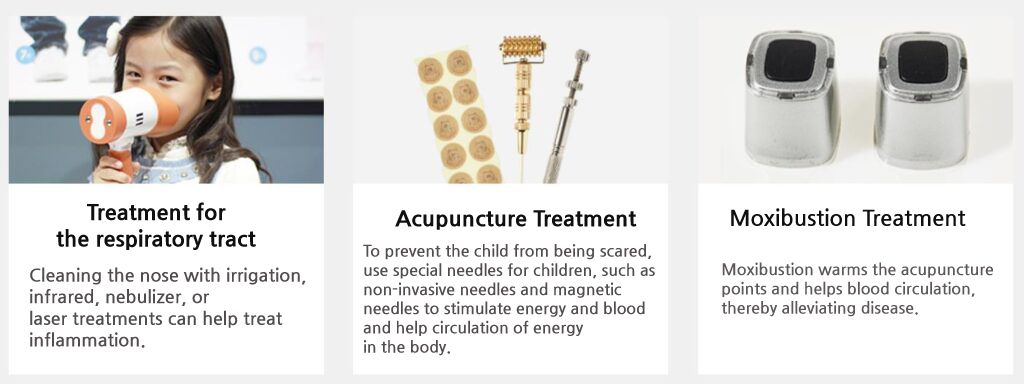

* Customized herbal formulas, syrup herbal formulas, etc., require a prescription after diagnosis by an Asian medicine practitioner.
* The treatment program requires treatment and consultation with the attending physician.

